If you are a practitioner in the field of advanced ceramic or a follower of this industry, this article will help you get a quick and holistic view of the entire advanced ceramics field.
What is advanced ceramic?
Advanced ceramics are other ceramics, as opposed to traditional architectural ceramics and household ceramics, which are mainly used in the industrial field and often exist as components of industrial products. It is an indispensable component of industrial manufacturing products.
traditional ceramics and advanced ceramics
Traditional ceramics have gone through three stages of development, namely, pottery, primitive porcelain, porcelain, in which the selection and refinement of raw materials, kiln improvement and firing temperature, glaze discovery and use of traditional ceramics has made a major breakthrough and development, but traditional ceramics have not formed into a science, the products are mainly used in daily utensils, building materials, these traditional ceramics can not meet the modern technology in electronic, electrical, heat engine, energy, space, self-control, sensing, laser, communications, computers and other high-tech requirements, advanced ceramics thus emerged, it draws on the basic principles and processes of traditional ceramics to prepare a series of new ceramic materials.

These traditional ceramics can not meet the requirements of modern science and technology in electronics, electrical, thermal, energy, space, self-control, sensing, lasers, communications, computers and other high-tech requirements, advanced ceramics from this, which draws on the basic principles of traditional ceramics and technology, the preparation of a series of new ceramic materials, with some special features: mechanical, thermal, acoustic, electrical, magnetic, optical, superconductivity, etc., advanced ceramics compared to traditional ceramics, in raw materials, technology, and performance are very different.
advanced ceramic powder properties and process
The microstructure of advanced ceramics determines its performance to some extent, and the microstructure depends on the preparation process. Preparation process includes powder preparation, molding and sintering three main links, of which, powder preparation is the basis, powder, that is, a large number of solid particles of the collection system, is gas, liquid, solid state outside the third phase. Powder performance is good or bad, directly affecting the quality of molding and sintering, if the powder mobility is poor, serious agglomeration, coarse particles, in the molding, it is not possible to get a uniform texture, high densification, no defects in the billet, so that the sintering conditions are difficult to control.
The preparation methods of advanced ceramic powders are generally categorized into mechanical and synthetic methods. Mechanical method is the use of mechanical pulverization method to convert mechanical energy into the surface energy of the particles, from coarse particles to obtain fine particles method. This method is simple, low cost, and suitable for industrialized mass production. The disadvantage is that the crushing process is inevitably mixed with impurities, and it is not easy to produce fine particles with a particle size of 1um or less. Synthesis method is through the reaction, nucleation and growth of ions, atoms or molecules, collected and processed to obtain fine particles. This method has controllable purity and particle size, good uniformity and fine particles. The synthetic method can be further divided into solid phase, liquid phase and gas phase methods.
advanced ceramics properties
The precise definition of advanced ceramics highly summarizes its characteristics, i.e., Ceramics with excellent properties made from highly selected raw materials, with a chemical composition that can be precisely controlled, processed in accordance with manufacturing techniques that can be easily controlled, and with structures that can be easily designed.
Types of Advanced Ceramic
According to the performance and function of ceramics, advanced ceramics are divided into structural ceramics and functional ceramics.
Structural ceramics have physical and mechanical properties, as well as some thermal and chemical functions, suitable for use at high temperatures, giving full play to its high temperature resistance, corrosion resistance, high strength, high hardness and other excellent properties. Among them, structural ceramics are divided into oxide, carbide, nitride, boride, silicide and other types.
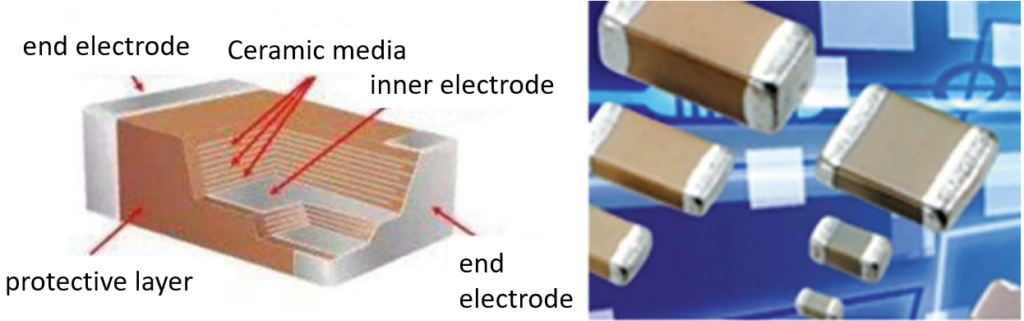
Functional ceramics are advanced ceramics with predominantly non-mechanical properties. Such ceramic materials usually have one or more functions, such as electrical, magnetic, optical, thermal, chemical, biological and so on. Some have coupled functions, such as piezoelectric, piezomagnetic, thermoelectric, electro-optical, acousto-optic, magneto-optic, etc.. Functional ceramics are often piezoelectric ceramics, superconducting ceramics, magnetic ceramics, bioceramics, nanoceramics.
With the development of science and technology, the emergence of new materials, structural ceramics and functional ceramics boundaries fade, some materials have both superior structural properties and excellent function. For example, silicon carbide is a common abrasive material, and can be used to do its semi-conductivity of high temperature heating elements.
Advanced Ceramics Application
Advanced ceramics because of its excellent physical and chemical properties, as well as thermal, optical, acoustic, electrical, chemical, biological and other non-mechanical properties, and some properties far more than modern high-quality alloys and polymer materials, advanced ceramics became the protagonist of the new materials technology in various industrial fields, such as petroleum, chemical, iron and steel, electronics, textiles, and automotive industries, cutting-edge technology areas such as aerospace, nuclear and military industries, there are a wide range of application value and potential.
Advanced Ceramic Molding Methods
Molding is the process in which the prepared billet is made into a billet with a certain shape and size through different molding methods. Before molding, the billet should meet certain requirements, such as fineness, moisture content, plasticity and fluidity. Because different ceramic parts for different purposes, the shape of the parts, size, material and firing temperature is different, the performance of the parts, quality requirements are also different, therefore, the molding method is also a variety of different. Molding methods can be categorized from the following aspects.
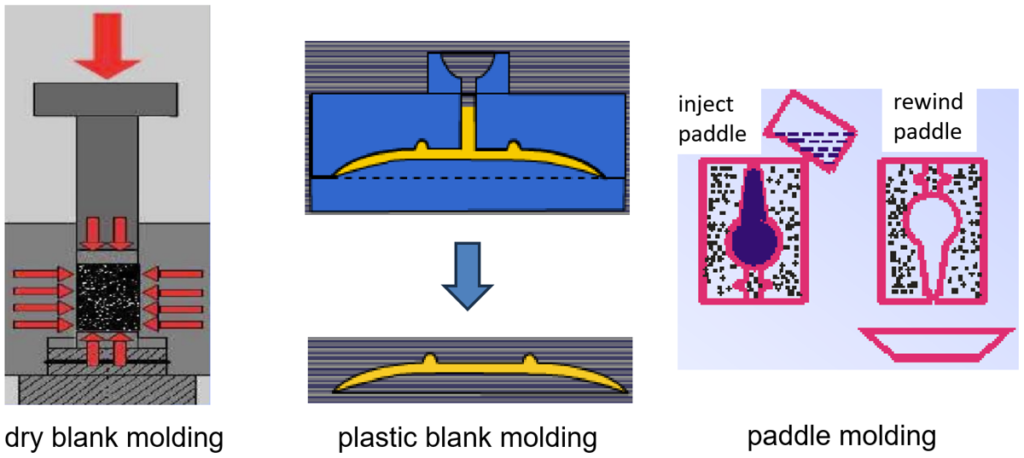
(1) According to the characteristics of the blank, according to the flow of the blank, rheological qualities, molding methods are divided into three categories: dry blank molding, plastic blank molding and paddle molding. In these three types of molding, mainly the water content of the embryo material is different, dry embryo material is basically water-free or less than 7%, the water content of the plastic embryo material is not more than 20% -30%, the paddle material has the largest water content, the conventional 28% -35%.
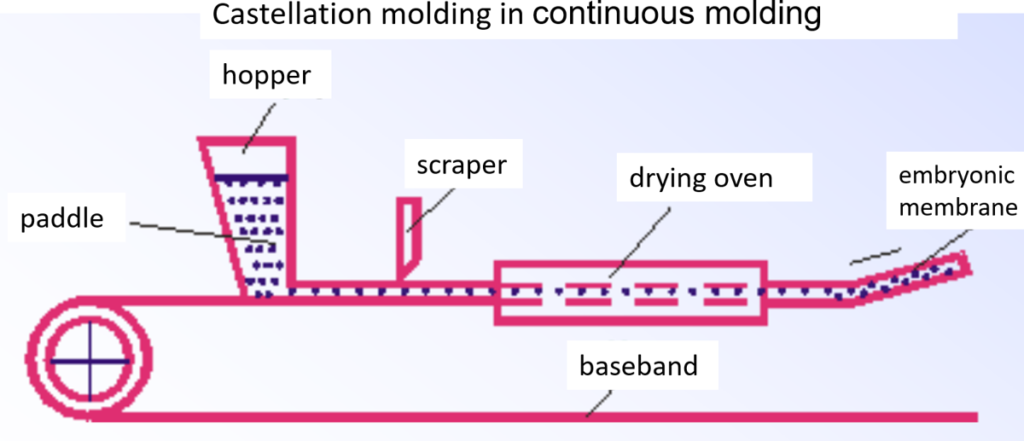
(2) according to the continuity of molding classification: continuous molding, discontinuous molding. Continuous molding refers to the billet for the continuous, consistent cross-section size of the band, bar or tube, etc. In actual production, often cut the billet into a certain length after molding, or sintered with a continuous sintering furnace and then cut to a certain length.
(3) Classified according to the presence or absence of molds: molded and moldless molding. Molding method with the shape and size of the blank molded by the mold to determine the mold material is metal, there are also non-metallic. The previous continuous molding method can also be categorized as moldless molding.
Molding method selection should be based on the drawings or samples to determine the process route, the choice can take into account several aspects: the shape and size of the parts themselves and the thickness of the blanks, blanks, process performance, the production of parts and quality, in order to ensure the quality of the product and the production of the premise, the choice of equipment is simple, the lowest cost of one.
Advanced Ceramic Sintering Methods
The process of sintering is the process of sintering the molded billet at a specific temperature, pressure, atmosphere, after a series of physical and chemical changes, to obtain a certain crystalline phase composition and microstructure of the sintered body. The purpose of sintering is to densify the molded billet to obtain the expected microstructure, giving the material a variety of properties.
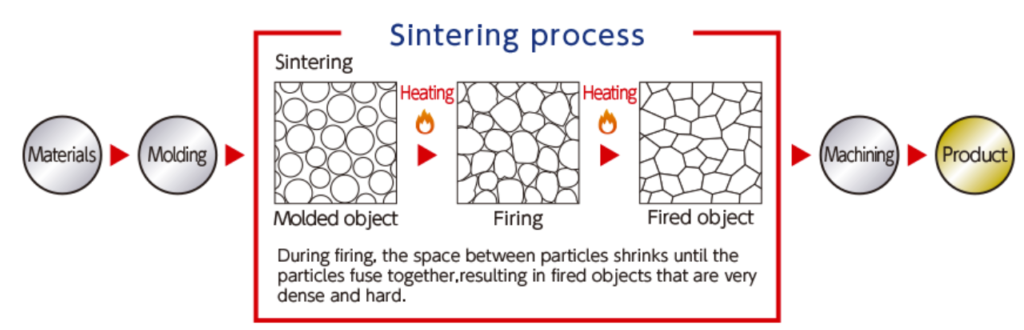
There are several sintering methods:
(1) Low-temperature sintering, the preparation of ceramics at the lowest possible temperature can reduce energy consumption and make the product cost lower. The main considerations are the introduction of additives and the use of powders that are easy to sinter.
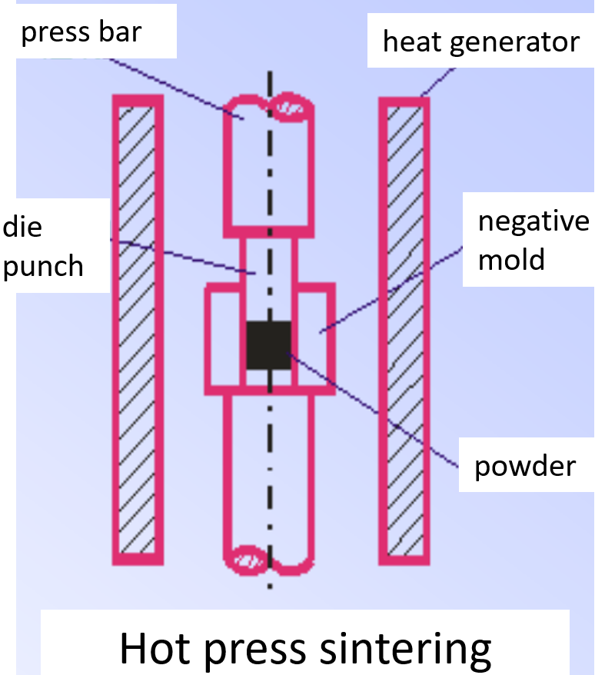
(2) hot pressure sintering, is to heat the powder at the same time as the pressure, when the sintering depends mainly on the plastic flow, rather than diffusion.
(3) hot isostatic pressing method, is the powder billet or loaded into the package sleeve of powder into a high-pressure container, so that the powder is subjected to high temperature and balanced pressure, was sintered into dense parts.
(4) Atmosphere sintering, for the air is difficult to sinter products (such as translucent or non-oxide), in order to prevent its oxidation, can be in the furnace chamber into a certain gas, the formation of the required atmosphere for sintering.
(5) other new sintering methods, with the continuous development of science and technology, some of the new advanced ceramic sintering methods continue to launch, such as discharge plasma sintering, explosive sintering, microwave sintering, electric field sintering, laser sintering and so on.
Cutting Technology for Advanced Ceramics
Advanced ceramics must be processed according to user requirements before application to become engineering components for use, because the sintered body size deviation is large, not up to the precision of the assembly, so it needs to be finish machining, and at the same time in the molding and sintering process, the surface of the products to varying degrees will be adherent, microwave ripples, and even the surface is wrapped by other compounds, so it is necessary to carry out the surface processing of the product treatment. Generally include cutting, grinding, finishing, special processing and other methods.
Cutting processing is usually carried out in three cases, precision and ultra-precision cutting of ceramic materials, cutting of pre-sintered ceramics or machinable ceramics, and special cutting of ceramic materials. For different kinds of ceramic materials, the corresponding tool materials are also different, commonly used tool materials are carbide, diamond, ceramic and CBN. carbide tools are mainly used for pre-sintered ceramics and machinable ceramics cutting processing. Diamond tools are most suitable for the processing of ceramic materials, ceramic tools are more suitable for the cutting of ceramic billets and machinable ceramic materials.
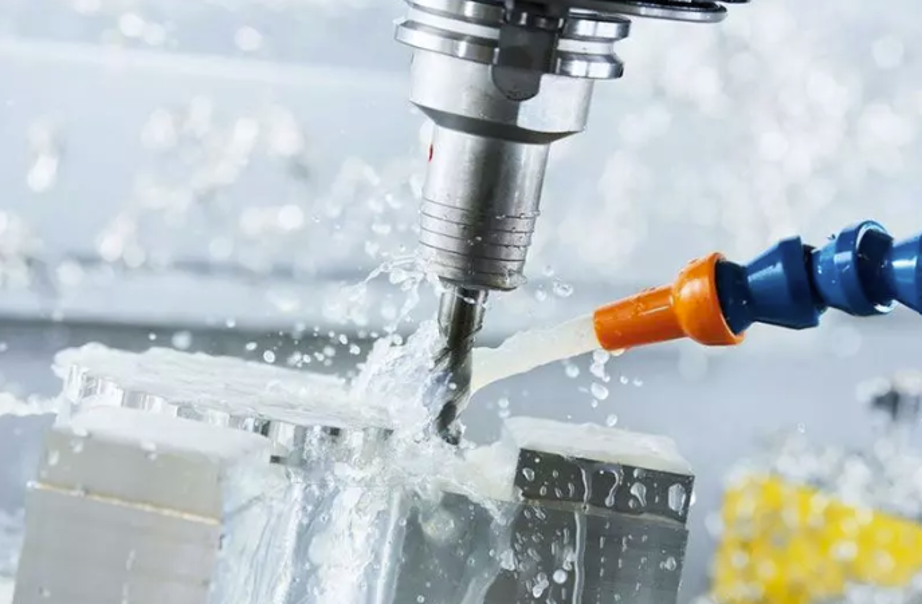

CBN tools have a very high thermal stability, used for the heating-assisted cutting of ceramic materials, but also can be used for cutting glass ceramics and alumina ceramics cutting. It is necessary to pay attention to the cutting characteristics of ceramic materials in terms of tool wear, cutting force, cutting temperature and cutting parameters during the cutting process.
Grinding Technology for Advanced Ceramics
Advanced ceramic grinding processing is a common ceramic processing method, in terms of grinding characteristics, the main aspects involved are grinding force, grinding specific energy, grinding temperature, grinding surface morphology, surface roughness, specific grinding stiffness and grinding ratio. The grinding process generates grinding residual stresses both on the ceramic surface and in the vertical grinding direction. The surface residual compressive stress helps to improve the bending strength of the material, which is favorable to the use of the material.
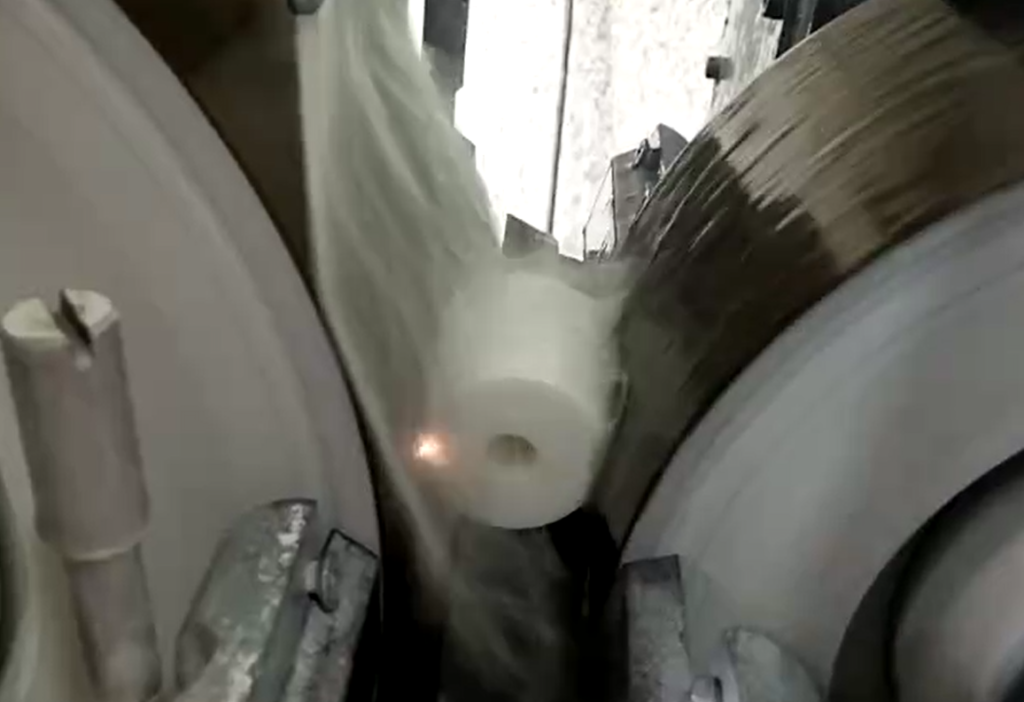

Special Processing Technology for Advanced Ceramic
Special processing technology, ultrasonic processing is with the emergence of a variety of brittle materials and difficult to process materials, and the application of the development of the integrated results through the mechanical impact of abrasive particles in the role of ultrasonic vibration and abrasive action, ultrasonic cavitation and hydraulic impact effect. Among them, the continuous impact of abrasive particles is the main one.
EDM processing is through the tool electrode and workpiece spark discharge generated by the local high temperature, high pressure to erode the workpiece material, processing is not limited by the hardness of the material, the workpiece and the tool between the macro force.
Laser processing is the use of laser's high brightness and high directionality, the light energy is concentrated in a certain range of space, so as to obtain a relatively large optical power density, resulting in thousands of degrees to tens of thousands of degrees above the high temperature, the high melting point of ceramic materials melting or even vaporization.
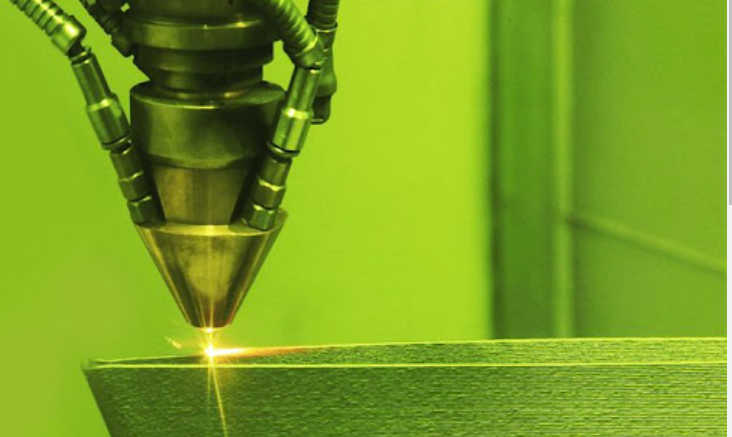

Advanced Ceramics Market and Future
From the end of the 19th century, mankind successfully synthesized silicon nitride and silicon carbide, advanced ceramics began the prelude to modern technology and civilization, higher purity ceramic raw material synthesis technology and sintering process was initially formed. 1970s began to set off a wave of advanced ceramics around the world heat, some new advanced ceramic materials and processes developed and applied to related fields. The United States and Japan in the advanced ceramics R & D level leading the world, the market scale continues to expand, the emergence of many in the field of advanced ceramics leading enterprises. Domestic head of the enterprise is relatively less, more are some small and medium-sized enterprises and research institutes. As the three basic materials, advanced ceramics will have more progress and application.
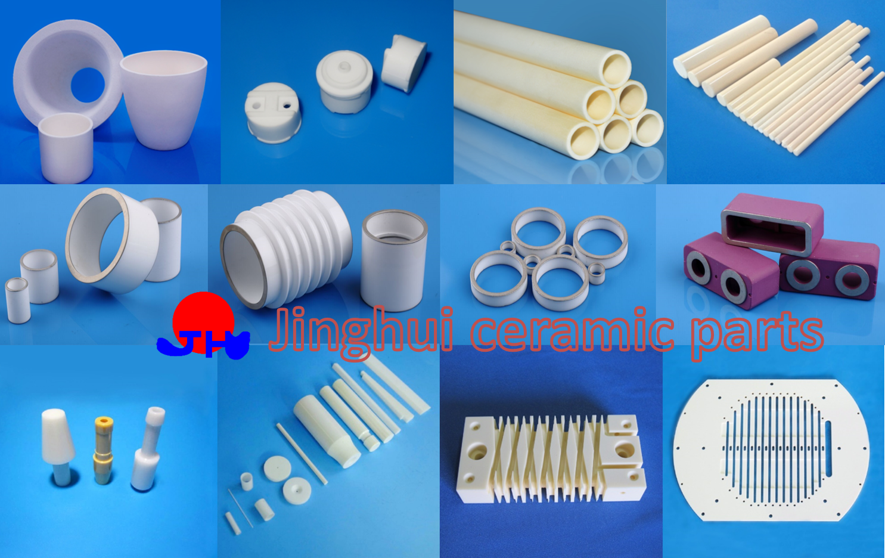

Jinghui as a manufacturer engaged in advanced ceramics, the purpose is to be a valuable supplier to customers in the advanced ceramics industry. We mainly provide metallized ceramics for circuit connections, ceramic grinding cores for coffee grinders, ceramic substrates for PCB boards, and engineered structural ceramics for components in various industries, and we will have high quality products and quality to help you take your business to the next level. If you are interested, please feel free to contact us at sales@jinghui0738.com

