Heat Dissipation is the Key to LED Development.
LED (Light-Emitting Diode) is a semiconductor light source. Its working principle is to use the characteristics of semiconductor materials to produce light under the action of electric current. LED has the advantages of high efficiency, long life, and low power consumption, and is widely used in lighting, display, communications and other fields.
With the continuous evolution of LED materials and packaging technology, the brightness of LED products continues to increase, and brightness is linked to power. The higher the power, the higher the temperature. Since only 15% to 20% of the input power of high-power LEDs is converted into light, and the remaining 80% to 85% is converted into heat. If this heat is not discharged to the outside in a timely manner, the temperature of the LED die interface will be too high and it will affect the luminous efficiency and luminous life.

Main Heat Dissipation Substrate
There are three main types of heat dissipation substrates used in the high-power LED industry, aluminum substrates, alumina ceramic substrates and aluminum nitride ceramic substrates.
- Aluminum substrate: A kind of metal substrate. The thermal conductivity is higher than that of plastic substrate. If it is used for high-power LED, it needs a better heat dissipation design to match. Otherwise, the junction temperature will still be very high and it will lead to light attenuation. Over time, the brightness of the LED lamp will decrease sharply, and the cost of the fan radiator in the heat dissipation design will be much higher. Compared with the ceramic substrate, an additional insulation process is required.
- Alumina ceramic substrate: The most widely used ceramic substrate. It has lower cost and its thermal conductivity is 10 times that of aluminum substrate. Taking the application of automotive LED headlights as an example, it is reasonable to say that it is sufficient as a headlight substrate. But people’s most intuitive concept of car lights is whether they are bright enough, so carmakers will naturally find ways to increase the brightness. Nowadays, the LED power of automobile headlights ranges from 20W to 60W. As the brightness increases, the power also increases, and the alumina ceramic substrate is no longer enough.

- Aluminum nitride ceramic substrate: The thermal conductivity is 5-7 times that of alumina ceramic substrate, making it the best choice for high-power LEDs.
Metallization Process
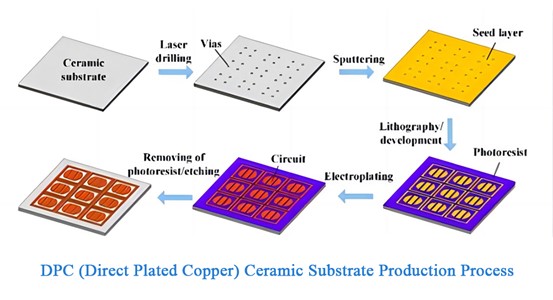
There are four main types of LED ceramic substrates that are widely used: thick film ceramic substrates (TFC), multilayer co-fired ceramic substrates (HTCC/LTCC), direct bonded copper ceramic substrates (DBC) and direct plated copper ceramic substrates (DPC). Among them, the DPC ceramic substrate has excellent thermal conductivity, high line alignment accuracy, stable chemical properties, and high mechanical strength. It is most suitable to apply DPC technology to the preparation of aluminum nitride (AlN) ceramic substrates, which can give full play to the excellent physical properties of AlN ceramics. At the same time, its preparation process temperature is low, which completely avoids the damage or dimensional variation caused by high temperature to the material, and also reduces the preparation cost of the substrate. Therefore, the AlN-DPC ceramic substrate is easier to meet the conditions for high-density packaging than other substrates. The process flow of DPC is shown in the figure below.
If you are interested in the application of aluminum nitride ceramic substrates in high-power LEDs, please contact us for more information.

