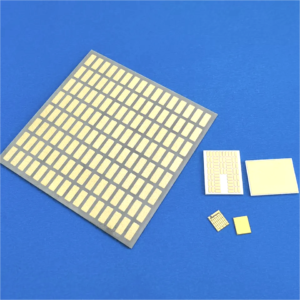
Surface Treatment of Ceramic Substrate
The purpose of plating gold on the surface of ceramic substrates is to achieve electrical conductivity and improve the corrosion resistance of ceramic substrates. The following is the general process flow of the gold plating method on the surface of ceramic substrates.
1. Cleaning: First, the ceramic substrate needs to be thoroughly cleaned to remove dirt and impurities on the surface. Ultrasonic cleaning or chemical cleaning methods such as pickling or alkaline cleaning can be used.
2. Surface activation: Next, the surface of the ceramic substrate needs to be activated to increase the adhesion of the metal deposition. A layer of active sites is usually generated on the surface using chemical methods, for example by treatment with an acidic solution such as dilute nitric or sulfuric acid.
3. Bottom layer deposition: After the surface activation treatment, the bottom layer metal is deposited first, such as nickel or copper. The underlying metal can provide better adhesion and conductivity while preventing the diffusion and reaction of the metal.
4. Metal deposition: After the bottom layer is deposited, the metal deposition on the surface, such as gold or silver, is carried out. Metal deposition can be achieved by electrochemical methods (electroplating). The ceramic substrate is immersed in an electrolyte solution containing gold or silver ions, and the metal ions are reduced to metal deposits on the surface of the ceramic substrate through the action of an electric current.
5. Post-processing: After the metal deposition is completed, the ceramic substrate needs some post-processing steps to improve the quality and stability of the gold-plated layer. For example, polishing, heat treatment, or encapsulation can be performed to obtain a uniform, dense, and corrosion-resistant metal coating.
Jinghui Ceramic has more than 15 years of experience in manufacturing metallized ceramic substrates. In addition to price advantages, we can also provide customers with small batch trial production and proofing services.

Product Feature
After gold plating, the ceramic substrate has many excellent properties and characteristics.
1. Excellent electrical conductivity. Current can flow freely across the substrate surface. This makes the substrate an ideal carrier for electronic devices, capable of efficiently conducting and distributing current and providing the necessary circuit paths for the device to function properly.
2. Excellent welding performance. The gold layer can provide good solder contact performance, so that the device can be easily connected with other components. This reliable solder contact helps to ensure the stability and reliability of electronic devices during operation, reducing possible problems such as resistance, poor contact or disconnection.
3. Good corrosion resistance. The gold layer can prevent the substrate from external corrosion, which effectively protects the stability and durability of the substrate and prolongs its service life.
4. Can withstand high temperature environment. This makes gold-plated ceramic substrates ideal for many high-temperature applications, such as power electronics, high-power LEDs, etc.
Product Application
The following are some application examples of gold-plated metallized ceramic substrates.
1. Electronic components: Widely used in the manufacturing process of various electronic devices such as integrated circuits, power modules, sensors, capacitors, etc.
2. Circuit board: Used to produce high-performance, high-reliability printed circuit boards (PCB). Gold-plated ceramic substrate provides good circuit transfer performance and stable soldering contact for high-frequency, high-power and high-temperature applications.
3. Optoelectronic device: Used as a heat dissipation base for high-power LEDs, which can effectively dissipate heat and improve the brightness and life of the LED. In addition, gold-plated ceramic substrates are also used in fields like laser diodes and optical fiber communication devices.
4. High temperature application: Used in the manufacturing of electronic devices in high temperature environments. For example, power electronic equipment, aerospace equipment, and gas burners require substrates with good high temperature resistance.
5. Biomedical field: Used as substrate and contact carrier for biosensors, medical devices, etc. It has good biocompatibility and conductivity, and can improve the performance and stability of medical devices.