With the continuous development of advanced ceramics, especially electronic ceramics, ceramics and metal connection has become a hot spot of people’s attention, but the surface of ceramic materials and metal surfaces are different microstructures, the use of the relevant solder to connect, the solder is not able to wet the surface of the ceramics, can not be well bonded with the ceramic surface, the study of ceramics and metal connection of the special process methods, that is, the ceramic metallization is the first ceramic surface to go to the surface of the firmly adhering to a layer of metal film, so as to allow ceramics and metal to achieve welding.
Principle of Ceramic Metallization
Chemical and physical reactions, plastic flow of substances, particle rearrangement, etc. are involved. Various substances such as oxides and non-metallic oxides in the metallization layer undergo different chemical reactions and substance diffusion and migration in different sintering stages. With the increase of temperature, each substance reacts to form intermediate compounds, and when they reach the common melting point, they form a liquid phase, and the liquid glass phase has a certain viscosity and produces plastic flow, after which the particles are rearranged under the action of capillaries, and the atoms or molecules diffusely migrate under the driving force of surface energy, and the grain grows up, and the porosity is gradually narrowed down and disappears, so as to achieve the densification of the metallization layer. 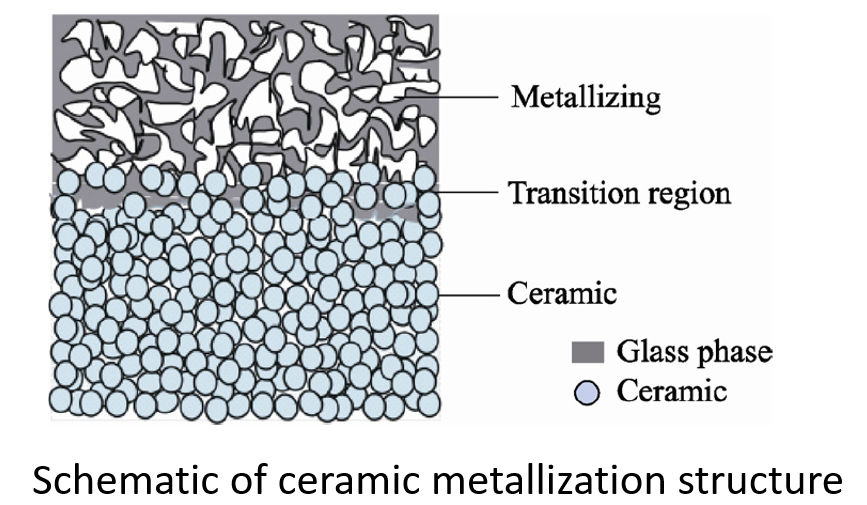 Process classification of metallized ceramics
Process classification of metallized ceramics
The discussion of metallized ceramics in this paper is devoted only to the metallization of advanced ceramic parts other than ceramic substrates.
1. Being silver method
Also known as burnt infiltration of silver method, is in the ceramic surface burnt infiltration of a layer of metallic silver, because of the strong conductive ability of silver, good oxidation resistance, you can directly weld the metal on the silver surface. Silver at high temperatures, high humidity and DC electric field, easy to diffuse into the medium, so being silver method should not be used in the electrical performance requirements of the environment to prevent the deterioration of electrical properties.
The specific process flow is shown below: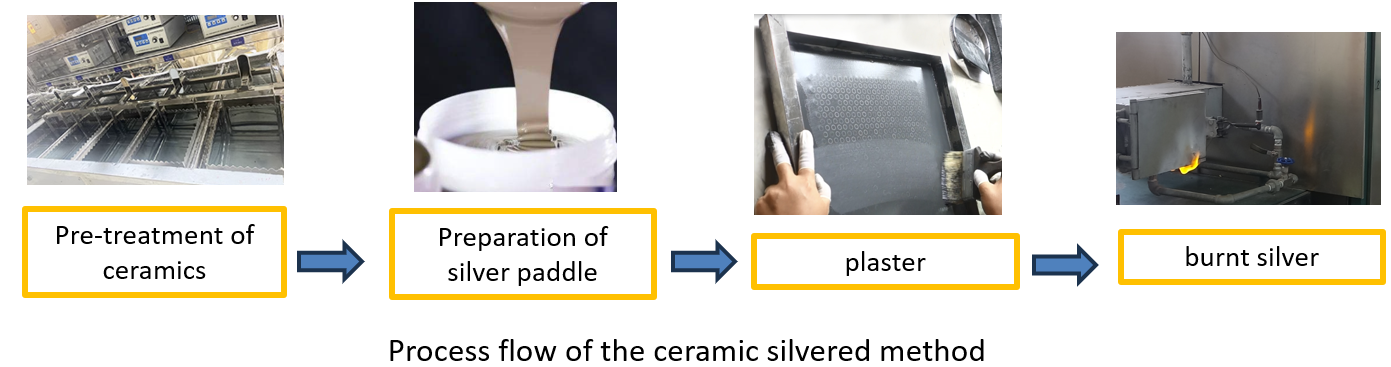
Pre-treatment of ceramics that is purification treatment, usually in 70 ~ 80 degrees of soapy water immersion, and then rinse with water. Also available ultrasonic vibration cleaning, cleaning to be dried in the oven at 100-110 degrees.
Silver-containing raw materials, flux and binder according to a certain ratio of ingredients, in the corundum ball mill tank ball mill 70-90h, to achieve a certain degree of fineness and mixing uniformity.
There are more methods of silver coating, such as manual, mechanical, dip coating, spraying and screen printing. Coating can be added to the appropriate amount of solvent, such as turpentine, etc., to adjust the thinning of the silver paddle.
Burning silver before the oven at 60 degrees to dry the silver layer, so that part of the solvent volatilization, so as not to burn the silver layer of silver scaly skin, and then put into the box-type electric furnace or electric tunnel kiln burn seepage.
2. Sintered metal powder method
Sintered metal powder method, is in a high-temperature reducing atmosphere, so that the metal powder in the ceramic surface sintered into a metal film, and then ceramic and metal sealing method.
This method needs to pay attention to two points, 1) to be welded to the melting point of the metal parts should be higher than the metallization temperature of more than 200 degrees, the solder, the composition of the metal parts should not be and the metal in the metallization of the metal to form alloys. 2) the expansion coefficient of the metal parts and the expansion coefficient of ceramics as close as possible to each other, match each other.
Sintered metal powder method used in the metal powder, usually a refractory metal powder (such as W, Mo) as the main, plus a small amount of lower melting point of the metal powder (such as Fe, Mn or Ti), the first invention of the formula is a mixed powder W-Fe, later invented a mixed powder Mo-Mn adaptability is stronger, and has been rapidly promoted. At present, the majority of units choose Mo-Mn formula, so it is also commonly known as the Mo-Mn method.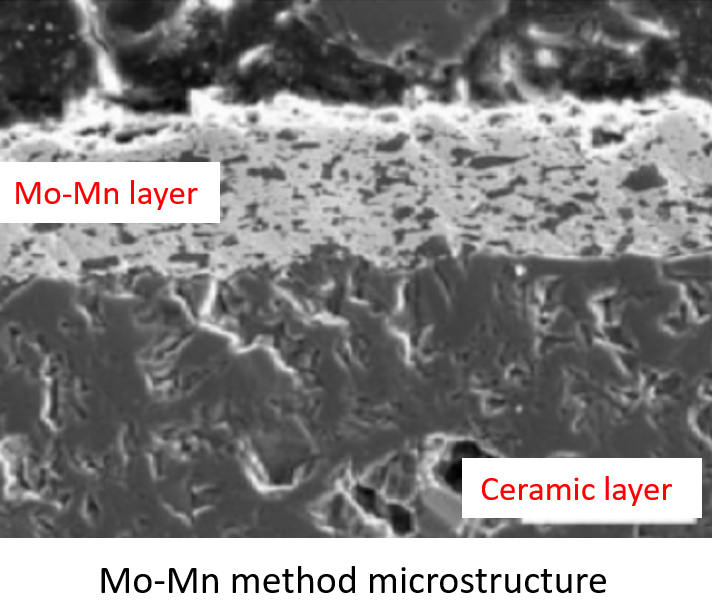
It can be roughly divided into two categories:
l) Add activator
Also known as activation Mo-Mn method, the purpose of adding activator in the metallization powder formula. Usually is to make the metallization temperature lower, so that ceramic metallization easier. Higher purity ceramics are not used when the activator, can make the sealing strength. Activator can be ore powder, porcelain powder, the main industry raw materials and chemical reagents. Activators mainly promote the production of high-temperature liquid phase. Before reaching the metallization temperature, some of the activator itself into a liquid phase, some with the ceramic part of the composition of the liquid phase, some with the oxidized metal powder to generate a liquid phase, these liquid phase at the same time infiltrated with metal powder and ceramic surfaces, and the role of the bonding.
2) Substitution of molybdenum and manganese oxides or salts for metal powders
The purpose of this type of method is to reduce the metallization temperature greatly, sometimes also called low temperature metallization method. Selected raw materials are mainly chemical reagents, such as MoO3, MnO2, (NH4)2MoO4, Mn(NO3 ) 2, KMnO4 and so on. Metallization temperature is generally below 1200°c. In addition to the metallization temperature is very low, because there is no metal powder in the formula, the density of each component does not differ much. It is easy to maintain a uniform composition, some formulations are completely water bath solution, and thus for the coating of deep and small holes is very convenient. Some formulations can make metallization and pin welding in a temperature rise completed. The main disadvantage is that the metallization layer migration rate is too high, not easy to control, sometimes the entire surface of the ceramic metallization layer. Formulation to add Cu2O on the migration of the metallization layer has an inhibitory effect, but it is difficult to achieve complete control, and sometimes must have been metallized porcelain parts of the grinding process, the parts do not need to be metallized, but has been migrated to the metallization layer grinding off. Then nail welding. Therefore, the field of application is limited.
In this type of method, no matter what form of molybdenum added, in the metallization of molybdenum metal after the vast majority of the reduction of molybdenum. This method has a very thin metallization layer and is mostly used for metallizing small parts or deep holes.
3、Active metal brazing method
It is 10 years later than the development of Mo-Mn method, characterized by fewer procedures, ceramic-metal sealing can be completed with only one heating process. Brazing alloy contains active elements, such as Ti, Zr, Hf and Ta, added active elements and Al2O3 reaction, the formation of a reaction layer with metal properties at the interface, this method can be easily adapted to large-scale production, compared with the molybdenum-manganese process, this method is relatively simple and economical. The disadvantage of the active metal brazing method is that the active brazing material is single, resulting in its application is somewhat limited, and is not suitable for continuous production, only suitable for large, single-piece production or small batch production.
4、Oxide solder method
With mixed oxides as solder for ceramic – metal sealing method, constitute the solder oxide must contain alkaline earth metal oxides, such as CaO, MgO, SrO, BaO, etc., at the same time must contain “acidic” or “neutral” oxide, such as SiO2, B2O3, Al2O3, etc.. ” oxides, such as SiO2, B2O3, Al2O3, etc.. These oxides can be melted first after quenching and then ground into fine powder, but also can be mixed oxides after grinding fine. Oxide solder method is mostly used for high alumina porcelain or transparent alumina porcelain and W, Mo, Ta, Nb and other metal sealing. Sealing, pure metal surface molecules partially oxidized into a low-value oxide and to the molten oxide diffusion. Formation of sealing layer.
5、Pressure sealing
Pressure sealing means that at room temperature, by mechanical pressure to make ceramic and metal strong pressure together to achieve airtight joint method. It utilizes the high compressive strength of ceramics and high-strength metal elastic deformation characteristics. The ceramic ring end face grinding out small oblique angle (7 ° ~ 10 °), and then use the inner diameter of the ceramic ring than the outer diameter of the metal ring is slightly smaller than the ceramic ring, the strong pressure on the outside of the ceramic. Ceramic compressive strength is high, forcing the metal ring expansion, as long as the elastic limit of the metal material, metal parts that is tightly clamped to the ceramic ring, the formation of pressure sealing. The sealing pressure can reach 600MPa.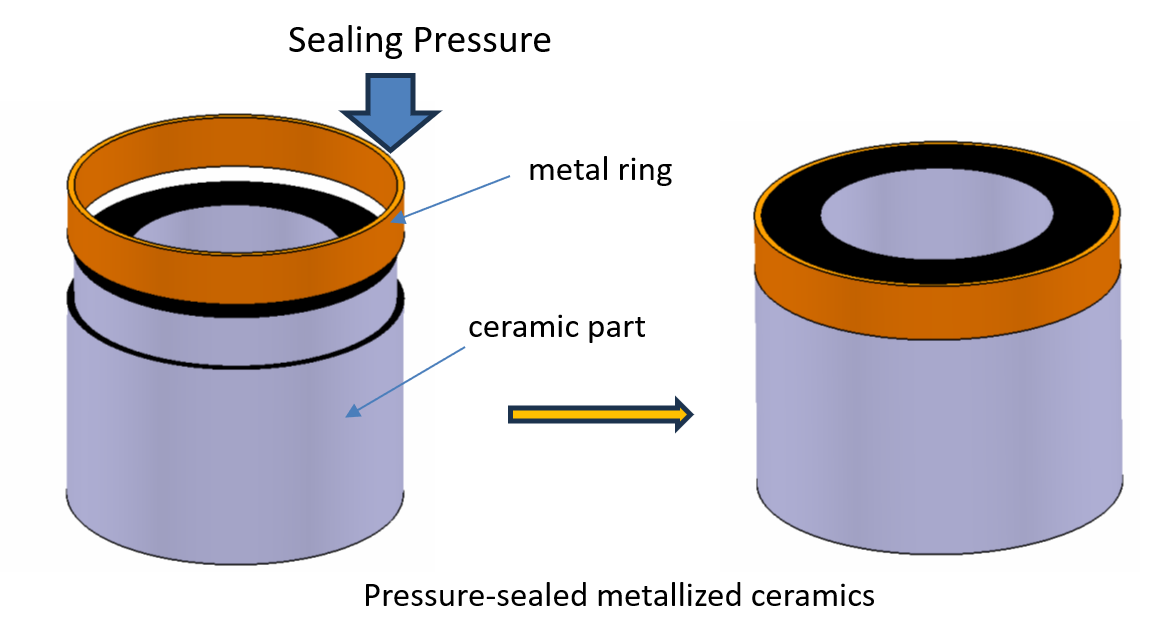
This process is mostly used for sealing parts with large volume and small quantity. Ceramic is basically high alumina porcelain, the metal used should have high strength, high elasticity, linear expansion coefficient approximate to ceramic, and good fatigue resistance. In the metal sealing surface, it is best to plating a layer of soft metal, not only is conducive to the set of sealing when the sliding, but also to ensure that the weld seam airtight. This plating is generally more silver, copper or gold.
6、Sputtering method metallization
Sputtering metallization is carried out in a vacuum system. There are two sputtering, four sputtering, high-frequency sputtering and other processes. Two sputtering is the most simple and the basis of the sputtering process. First the system is pumped into 10-5 Pa high vacuum. And then filled with argon, the pressure is maintained at 1 ~ 10-1Pa, ceramic parts placed near the sputtering target. When the sputtering target plus 1 ~ 7kV negative high voltage. Argon will be ionized first, positive ions high-speed bombardment to the target surface. The target surface metal sputtering, deposited on the ceramic surface. Formation of metal film.
The metal target is generally two or three different metals installed in the system can be freely rotated on the shelf. After sputtering the first layer of metal. After sputtering the first layer of metal, turn the target frame, and then sputter the second layer of metal. The first layer of metal with tungsten or molybdenum, sputtering layer should be dense, thickness of about 50 ~ 500nm, the second layer of copper, silver or gold and other insoluble in the first layer of the metal, the thickness can be l ~ 5 um. The first layer of metal using Ti, the effect is better.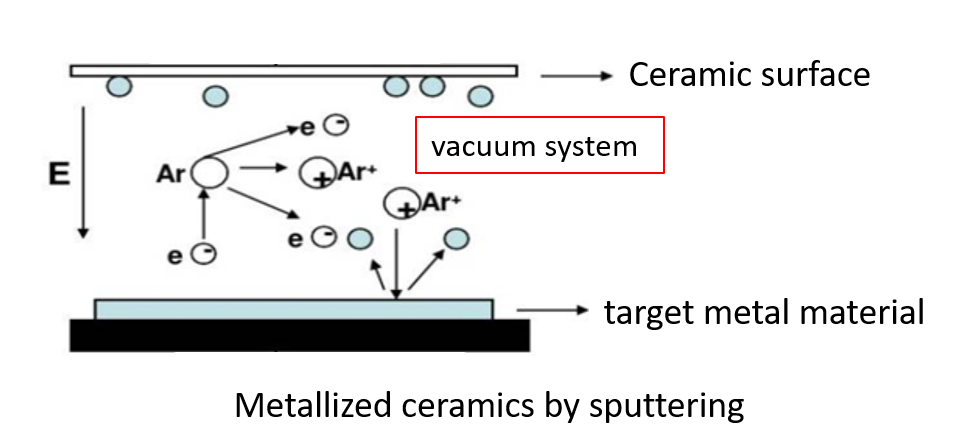
Metallization of ceramics by sputtering. Ceramic surface temperature is very low, more suitable for ceramics that can not withstand high temperatures (such as piezoelectric ceramics, etc.) for metallization, and the metallization layer is very thin, to ensure that the parts of the precision size requirements.
Technical challenges of metallized ceramics
1) The thermal expansion coefficients of ceramics and metals are quite different, which can easily lead to stress during the sintering process, resulting in cracking and destruction of the ceramic metallized layer.
2) There are certain chemical reactions at the bonding interface between the metal and the ceramic that produce oxides, which lead to changes in the chemical composition and structure of the interface, affecting the performance of the ceramic metallized layer.
3) The melting points of the ceramic and the metal are also quite different, which makes the sealing It is difficult to realize complete fusion. This will lead to tiny cracks and defects at the sealing interface, which will reduce the strength and sealing of the sealing.
4) The high cost of ceramic metallization technology and the complexity of the manufacturing process have limited its application in some fields.
The Future of Metallized Ceramics
By combining metal materials with ceramic materials, the deficiencies in electrical conductivity, thermal conductivity and mechanical properties of ceramic materials themselves can be overcome, which has a wide range of application prospects in aerospace, energy, electronic devices and other fields. In the future, the application areas can be further expanded, such as medical devices, automobile manufacturing, etc., to meet the needs of different fields.
Jinghui is a professional enterprise engaged in the research and production of precision ceramics, our metallized ceramic products are commonly used raw materials such as alumina, zirconium oxide and aluminum nitride, etc. The main process is silvered and sintered metal powder method. The main process is silvered and sintered metal powder method, we can provide silver, silver-palladium, molybdenum-manganese, tungsten and other materials for surface metallization of ceramics, and at the same time can be plated on the surface of the metallized layer of nickel, tin, and gold and other metals with excellent solderability, and can be designed and produced according to the customer’s needs.

